Ship Building & Repairing Industry - Market Research Report
Industry Overview
This U.S. industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in operating shipyards. Shipyards are fixed facilities with drydocks and fabrication equipment capable of building a ship, defined as watercraft typically suitable or intended for other than personal or recreational use. Activities of shipyards include the construction of ships, their repair, conversion and alteration, the production of prefabricated ship and barge sections, and specialized services, such as ship scaling. Illustrative Examples: Barge building Cargo ship building Drilling and production platforms, floating, oil and gas, building Passenger ship building Submarine building
Source: U.S. Census BureauMarket Size and Industry Forecast
This research report analyzes the market size and trends in the Ship Building and Repairing industry. It shows overall market size from 2020 to the present, and predicts industry growth through 2030. Revenues data include both public and private companies.
| Historical | Forecasted |
|---|
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 |
|---|
| Market Size (Total Revenue) | Included in Report |
| % Growth Rate |
| Number of Companies |
| Total Employees |
| Average Revenue per Company |
| Average Employees per Company |
Source: U.S. government financial dataIndustry Revenue ($ Billions)
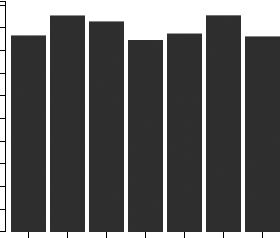
Industry Forecast ($ Billions)
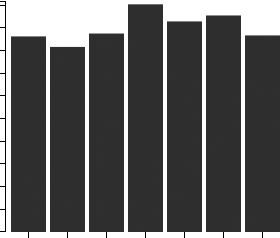
Advanced econometric models forecast five years of industry growth based on short- and long-term trend analysis. Market size includes revenue generated from all products and services sold within the industry.
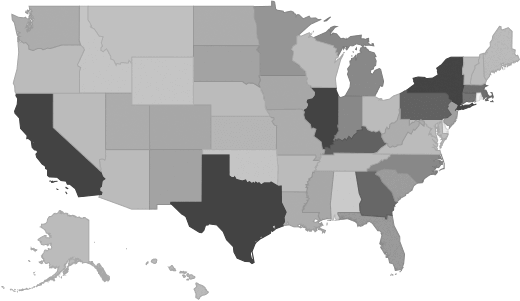
Geographic Breakdown by U.S. State
Market size by state reveals local opportunity through the number of companies located in the region. Each state's growth rate is affected by regional economic conditions. Data by state can be used to pinpoint profitable and nonprofitable locations for Ship Building & Repairing companies in the United States.
Ship Building & Repairing Revenue by State
Distribution by Company Size
| Company Size | All Industries | Ship Building & Repairing |
|---|
| Small Business (< 5 Employees) | Included |
| Small Business (5 - 20) |
| Midsized Business (20 - 100) |
| Large Business (100 - 500) |
| Enterprise (> 500) |
Ship Building & Repairing Industry Income Statement (Average Financial Metrics)
Financial statement analysis determines averages for the following industry forces:
- Cost of goods sold
- Compensation of officers
- Salaries and wages
- Employee benefit programs
- Rent paid
- Advertising and marketing budgets
The report includes a traditional income statement from an "average" company (both public and private companies are included).
| Industry Average | Percent of Sales |
|---|
| Total Revenue | Included |
| Operating Revenue |
| Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) |
| Gross Profit |
| Operating Expenses |
| Operating Income |
| Non-Operating Income |
| Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) |
| Interest Expense |
| Earnings Before Taxes |
| Income Tax |
| Net Profit |
Average Income Statement
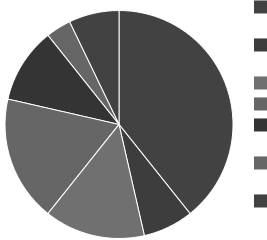
Cost of Goods Sold
Salaries, Wages, and Benefits
Rent
Advertising
Depreciation and Amortization
Officer Compensation
Net Income
Financial Ratio Analysis
Financial ratios allow a company's performance to be compared against that of its peers.
| Financial Ratio | Industry Average |
|---|
| Profitability Ratios | Included |
| Profit Margin |
| ROE |
| ROA |
| Liquidity Ratios |
| Current Ratio |
| Quick Ratio |
| Activity Ratios |
| Average Collection Period |
| Asset Turnover Ratio |
| Receivables Turnover Ratio |
| Inventory Conversion Ratio |
Products and Services Mix
Product lines and services in the Ship Building & Repairing industry accounting for the largest revenue sources.
| Product Description | Description | Revenue
($ Millions) |
|---|
Ship building and repairing | Included |
Ships, barges, and platforms, nonpropelled, new construction |
Ships, self-propelled, military, new construction |
Ships, self-propelled, nonmillitary, new construction |
Yachts, self-prop, nonmil, >= 65 ft (req prof. crew), new const. |
Commer. fish trawlers/ vessels (self-prop., nonmil., new const.) |
Tugboats/towboats, self-propelled, nonmilitary, new const. |
Ferryboats, self-propelled, nonmilitary, new construction |
Sup. vessels, offshore drill/mine, self-prop, nonmil, new const |
Ships, other types, self-propelled, nonmilitary, new const. |
Salary information for employees working in the Ship Building & Repairing industry.
| Title | Percent of Workforce | Bottom Quartile | Average (Median) Salary | Upper Quartile |
|---|
| Management Occupations | 4% | Included |
| Chief Executives | 0% |
| General and Operations Managers | 1% |
| Architecture and Engineering Occupations | 11% |
| Engineers | 8% |
| Office and Administrative Support Occupations | 7% |
| Construction and Extraction Occupations | 15% |
| Construction Trades Workers | 13% |
| Installation, Maintenance, and Repair Occupations | 7% |
| Production Occupations | 46% |
| Assemblers and Fabricators | 16% |
| Miscellaneous Assemblers and Fabricators | 12% |
| Fiberglass Laminators and Fabricators | 6% |
| Assemblers and Fabricators, All Other, Including Team Assemblers | 6% |
| Metal Workers and Plastic Workers | 16% |
| Welding, Soldering, and Brazing Workers | 10% |
| Welders, Cutters, Solderers, and Brazers | 9% |
| Other Production Occupations | 7% |
Government Contracts
The federal government spent an annual total of
$15,794,261,119 on the ship building & repairing industry. It has awarded 23,028 contracts to 1,040 companies, with an average value of $15,186,790 per company.
Top Companies in Ship Building & Repairing and Adjacent Industries
| Company | Address | Revenue
($ Millions) |
|---|
Included |



